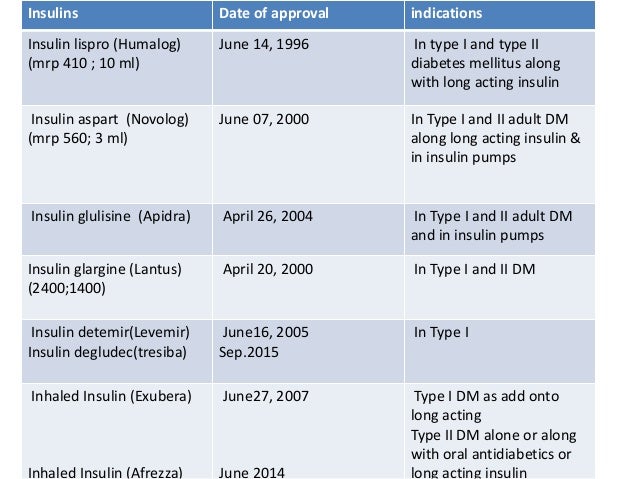
How you respond to insulin. Formulas commonly used to create insulin dose recommendations this example illustrates a method for calculating of your backgroundbasal and bolus doses and estimated daily insulin dose when you need full insulin replacement.
 Unit 4 Day 6 More With Piecewise Functions Ppt Download
Unit 4 Day 6 More With Piecewise Functions Ppt Download
when a diabetic takes long acting insulin is important information accompanied by photo and HD pictures sourced from all websites in the world. Download this image for free in High-Definition resolution the choice "download button" below. If you do not find the exact resolution you are looking for, then go for a native or higher resolution.
Don't forget to bookmark when a diabetic takes long acting insulin using Ctrl + D (PC) or Command + D (macos). If you are using mobile phone, you could also use menu drawer from browser. Whether it's Windows, Mac, iOs or Android, you will be able to download the images using download button.
However the intermediate or long acting insulin may not last a full 24 hours putting some users at risk for high blood sugar in the afternoon or evening.

When a diabetic takes long acting insulin. The insulin can take up to 4 hours to get into your bloodstream. On the day of the colonoscopy patients using intermediate or long acting insulin should be advised to take one third to one half of their insulin dose. Lets say you usually take 30 units of long acting and 10 units of short acting insulin.
It peaks in eight hours and works for 12 to 16 hours. A simple approach for starting mealtime insulin is to decrease the long acting insulin dose by 10 and take the difference as rapid acting insulin at dinnertime. Not many people are aware of the fact that an overdose of long acting insulin is far less dangerous than that of short acting or intermediate acting insulin.
What type of insulin is best for my diabetes. Includes a combination of either fast acting or short acting insulin with a longer acting insulin typically an nph insulin. Includes the analogues insulin glargine u300 and degludec which begin working within 30 to 90 minutes and continues to be active for greater than 24 hours.
Fast acting insulin can be used to correct hyperglycemia8 fasting holidays present a unique challenge. Taking too much insulin can lead to hypoglycemia this can become particularly serious if your insulin dose was significantly more than it should have been. Mealtime insulin should not be used until the patient eats.
How long it takes the body to absorb it and how long it remains active varies from. Making that choice will depend on many things including. Take insulin but dont eat.
Your doctor will work with you to prescribe the type of insulin thats best for you and your diabetes. Its easy to get them mixed up. Rapid acting and short acting insulin injections should be taken just before or.
Use the wrong type of insulin. This type takes the longest amount of time to start working. The total lunch insulin dose is 8 units of rapid acting insulin.
If you are wondering what happens if a non diabetic takes insulin here are some of the commonest symptoms that you would note. It is sometimes called regular acting insulin. Because intermediate acting insulin is not peaking during the day you have more flexibility with meal times.
For example if you previously took 20 units of glargine at bedtime you would take 2 units of aspart lispro or glulisine at dinner and 18 units of glargine before bed. The intermediate type takes one to three hours to start working. If you are worried that you have overdosed on insuli take ample fast acting carbohydrate immediately and seek advice from your health team or the out of hours service at your local.
 Piecewise Defined Functions Homework Student Copy Mth 135
Piecewise Defined Functions Homework Student Copy Mth 135
 Solved 1 Th A Typical Diabetic Taking Long Acting Insuli
Solved 1 Th A Typical Diabetic Taking Long Acting Insuli
 Solved 1 Th A Typical Diabetic Taking Long Acting Insuli
Solved 1 Th A Typical Diabetic Taking Long Acting Insuli
 Solved 1 Th A Typical Diabetic Taking Long Acting Insuli
Solved 1 Th A Typical Diabetic Taking Long Acting Insuli
 Long Acting Insulins For The Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes
Long Acting Insulins For The Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes
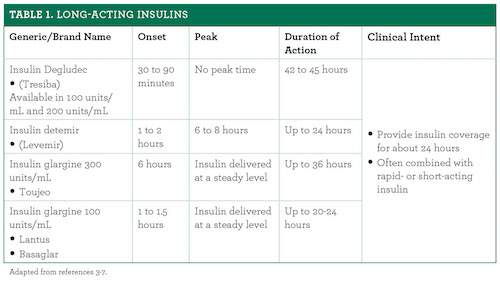 Long Acting Insulins Useful Tools In Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
Long Acting Insulins Useful Tools In Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes
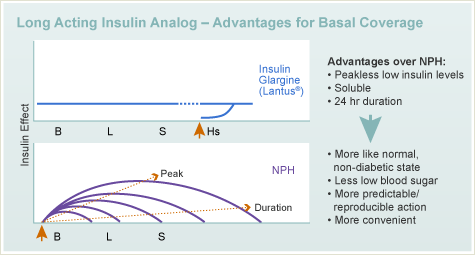 Insulin Analogs Diabetes Education Online
Insulin Analogs Diabetes Education Online
Management Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Requiring Insulin
 Management Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Requiring Insulin
Management Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Requiring Insulin
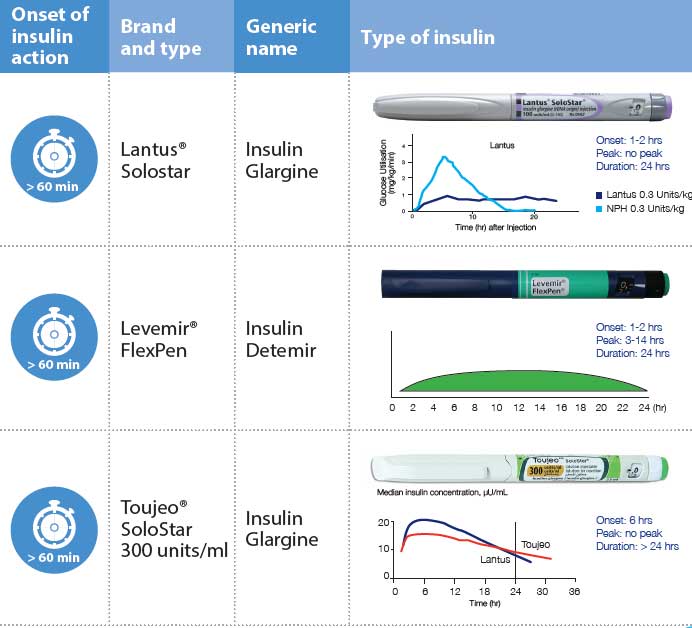 Types Of Insulin And Their Action Profiles
Types Of Insulin And Their Action Profiles