Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous syndrome characterized by abnormalities in carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Type 2 diabetes is far more common than type 1.
 Differentiation Of Diabetes By Pathophysiology Natural
Differentiation Of Diabetes By Pathophysiology Natural
what is the physiology of diabetes is important information accompanied by photo and HD pictures sourced from all websites in the world. Download this image for free in High-Definition resolution the choice "download button" below. If you do not find the exact resolution you are looking for, then go for a native or higher resolution.
Don't forget to bookmark what is the physiology of diabetes using Ctrl + D (PC) or Command + D (macos). If you are using mobile phone, you could also use menu drawer from browser. Whether it's Windows, Mac, iOs or Android, you will be able to download the images using download button.
Studies conducted on the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus suggested that abnormal metabolism of insulin hormone is the primary cause for the development of this complex syndrome.

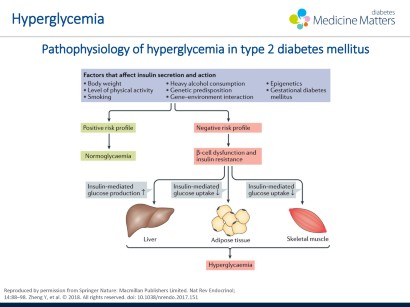
What is the physiology of diabetes. Type 2 diabetes mellitus consists of an array of dysfunctions characterized by hyperglycemia and resulting from the combination of resistance to insulin action inadequate insulin secretion and excessive or inappropriate glucagon secretion. Anatomy and physiology of diabetes. Most patients with gestational diabetes return to a normoglycemic state after parturition.
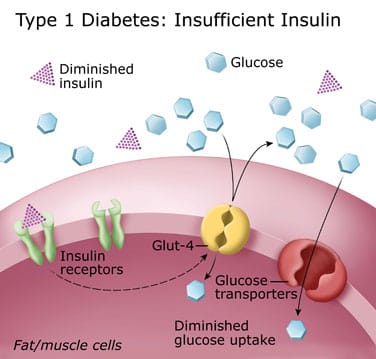
The brain and red blood cells depend on glucose almost exclusively. In type 2 diabetes the pancreas still makes insulin but the tissues do not respond effectively to normal levels of insulin a condition termed insulin resistance. The american diabetes association jdrf the european association for the study of diabetes and the american association of clinical endocrinologists convened a research symposium the differentiation of diabetes by pathophysiology natural history and prognosis on 1012 october 2015.
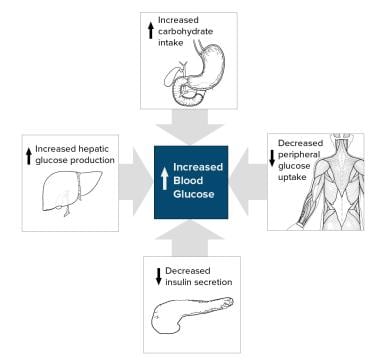
Diabetes occurs when there is a dis balance between the demand and production of the hormone insulin. Diabetes mellitus part 1. To keep the body running smoothly a continuous concentration of 90 to 100 mg of glucosedl of blood plasma is needed.
Diabetes occurs when there is a dis balance between the demand and production of the hormone insulin. Control of blood sugar. Poorly controlled type 2 diabetes is associated with an array of microvascular macrovascular and neu.
However about 30 to 50 of women with a history of gestational diabetes will develop type 2 diabetes within 10 years. It usually occurs in adulthood but young people are increasingly being diagnosed with this disease. It makes up most of diabetes cases.
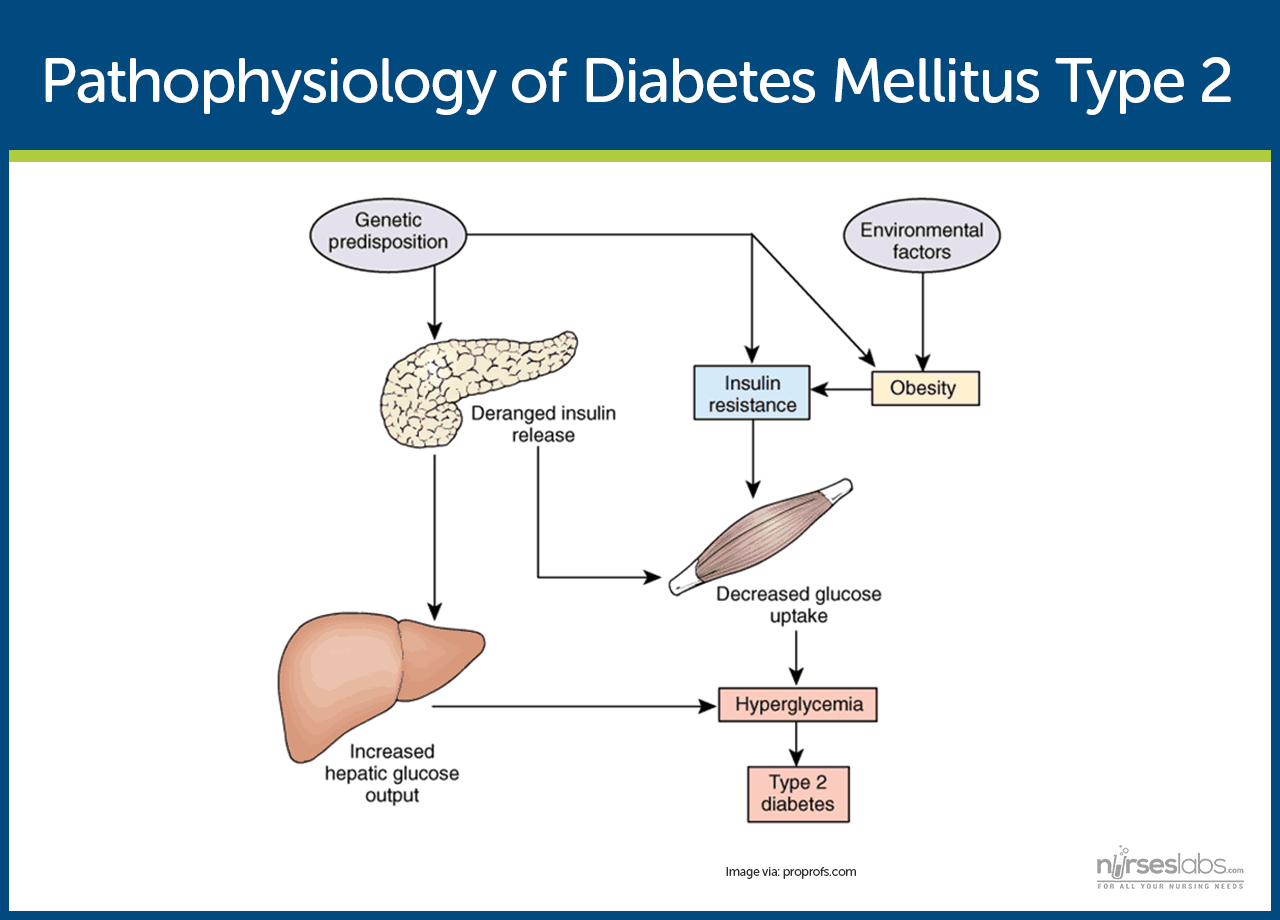
As with type 2 diabetes the pathophysiology of gestational diabetes is associated with increased insulin resistance. The number of people diagnosed with diabetes is approximately 18 million and an. The causes of type 2 diabetes are multi factorial and include both genetic and environmental elements that affect beta cell function and tissue muscle liver adipose tissue pancreas insulin sensitivity.
Throughout the body cells use glucose as a source of immediate energy. When food is taken it is broken down into smaller components. Physiology and complications abstract in part 1 of this 2 part article the author discusses the physiology and complications of diabetes mellitus dm a chronic and progressive disorder which affects all ages of the population.
Even though the etiologies and triggering factors of the three types of diabetes mellitus are different they cause nearly the same symptoms and complications. Pathophysiologic alteration is a change in function as distinguished from a structural defect. International experts in genetics immunology metabolism endocrinology and systems biology.
Physiology of type 2 diabetes normal regulation of blood glucose levels.
 Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care Management
Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care Management

Pathophysiology And Clinical Presentation Type 1 Diabetes
 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Practice Essentials Background
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Practice Essentials Background
 Pathophysiology Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus A 90
Pathophysiology Of Type 1 And Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus A 90
 Pathophysiology Of Diabetes Youtube
Pathophysiology Of Diabetes Youtube
 Pathophysiology Of Diabetes Mellitus
Pathophysiology Of Diabetes Mellitus
 Diabetes Type 1 And Type 2 Anatomy And Physiology I
Diabetes Type 1 And Type 2 Anatomy And Physiology I
A General Overview On Diabetes And The Physiology Behind It
 Etiology Pathogenesis Of Diabetes Mellitus
Etiology Pathogenesis Of Diabetes Mellitus
